Sponsors Article
Enterprise network technology from QCT for the 5G campus
In the industry, the combination of 5G networks and edge computing is currently the focus of interest. (Source: Pete Linforth/Pixabay)
High speed, reliability and low latencies – these are not just the demands of industry that should be met using private 5G networks. There are very similar requirements in the corporate network of large corporations. QCT uses its expertise to transfer the tried and tested technologies used there to 5G edge solutions.
5G edge networks are the drivers of the new cellular standard in the area of commercial applications, according to an analysis by ABI Research. Market researchers anticipate an increase in annual spending worldwide for 5G campus networks to more than 65 billion US dollars by 2030. Last year, the figure was a modest 1.6 billion dollars.
A key difference in the roll-out of the fifth generation of mobile communications is the focus on business models and the integration of vertical industries, states the report “Monetizing 5G Edge Networks: Different Approaches and Scenarios”. The problem is the inability to scale, because currently every project is a customer-specific solution. The development of viable business cases remains a key factor for the success of 5G projects.
As a result, building a 5G edge network is only the first step. In addition to installing the infrastructure, it is essential to find out how these new technologies can best be integrated into the business processes of vertical companies. This would require a convergence of services and process innovations in different areas to be initiated, says Don Alusha, Senior Analyst, 5G Core & Edge Networks at ABI Research.
Seamless end-to-end integration
The expansion of the IoT and the increasing use of machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), augmented and virtual reality (AR / VR) also in industry clearly show that digital transformation is also in discrete and process manufacturing Ride wins. Industrial 5G offers the reliability in connectivity, low latency and high bandwidths for data exchange between shop floor, edge devices and the cloud that are essential for such applications.
In the end, however, it is not just the radio technology that counts, but a smooth flow of data throughout the network. This is exactly where QCT (Quanta Clout Technology) comes in. The subsidiary of the globally active Quanta group uses its experience in the enterprise and provider segment to create end-to-end solutions for 5G private networks that are characterized by interoperability, easy deployment and high flexibility. Examples include virtualization technologies such as Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV), which enable extensive quality management in the network and thus minimize disruptions in the flow of data.
To simplify the management of network resources, QCT relies on an in-house automation and zero-touch provisioning container platform, as well as on open source standards from other technology partners, such as the Open Network Automation Platform (ONAP) or the OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) of the IBM subsidiary Red Hat. The provider optimizes the network from the data center to the edge and beyond to the cloud on the basis of its optimized hardware.
5G expansion of the company network
Open standards in hardware and software development, low energy consumption and easily accessible technology that simplifies the replacement or upgrade of components are design principles practiced by QCT that meet the requirements of industry to a high degree.
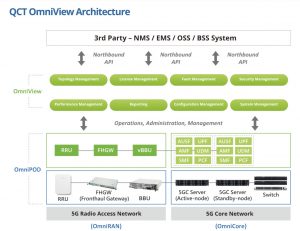
This also applies to the hardware portfolio for private 5G network solutions that QCT offers under the name OmniPOD Enterprise 5G. Highly available network technology is combined with a reliable 5G core and a flexible RAN system configuration. This covers all 5G application scenarios, from extended mobile broadband (eMBB) to massive machine-typical communication (mMTC) and ultra-reliable low latency (uRLLC).
The portfolio comprises three main components:
- QCT OmniCore: a cloud-native, virtualized 5G network solution that includes 5G core servers as well as data and management switches.
- QCT OmniRAN: The radio solution consists of a baseband unit (BBU), the front haul gateway (FHGW) and one to four remote radio units (RRU) per cell.
- QCT OmniView: The extensive network management system is used to configure and monitor hardware and software. The core tasks include topology management, performance management, security management and system administration.
QCT OmniView is one of the OAM solutions (Operations, Administration and Management). In addition to data, high-speed networks also transport standardized management information that is used for OAM functions. QCT OmniView enables greater efficiency in network operations, lower maintenance and management costs and enhanced security functions.
The 5G core QCT Omnicore is designed as a high availability solution (HA) that bypasses a single point of failure (SPOF) independently via switchover to a redundant component. The manufacturer states that the system can process data rates of more than 130 Gbit / s and can handle more than 10,000 participants – in production, for example, 5G-capable sensors and actuators.
The OmniRAN solution relies on virtualized radio access networks (vRAN), which were developed together with the technology partners Intel and Radisys. For example, Intel FlexRAN is integrated, a cloud-capable reference implementation of virtual network functions for wireless access. Likewise the Radisys Connect 5G RAN software, a disaggregated RAN architecture to support 4G, 5G and IoT.
“QCT works closely with its partners to ensure that customers can always stay ahead of the game.”
Mike Yang, President of QCT
The Quanta manager points to extensive expertise in various industries. In the industrial environment, for example, QCT OmniRAN is used in 5G networks in which the environment is monitored by video by a security AI. Other applications include high-resolution streaming in quality control, AR glasses for maintenance and repair, and driverless transport systems (AGV) in intralogistics.