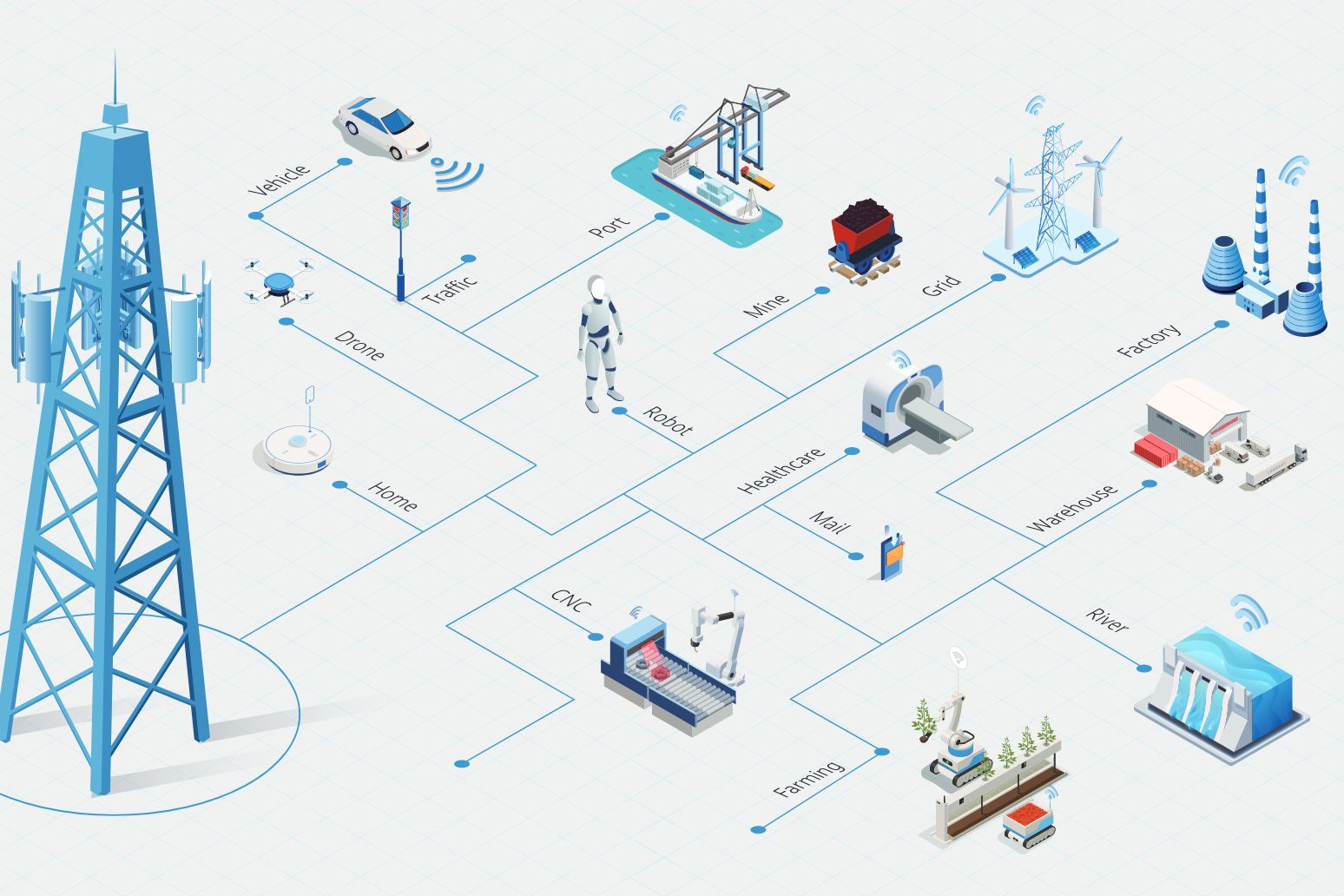
Low latency and high reliability are arguments for the use of 5G in many industries, such as process control and machine collaboration. (Picture: Screenshot Whitepaper Huawei)
Since the early days of 5G, one of the key messages has been that this standard is not only predestined to improve the consumer experience on mobile phones. Rather, all industries and sectors of the economy will benefit from the new mobile standard sooner or later. This article highlights ten of the key trends that will make 5G a game-changer.
5G will play a strong role in making the digital economy a major driver of the real economy by 2030. In addition, the industry will shift its focus from device efficiency to decision efficiency. David Wang is convinced of these two developments. While Wang, as Executive Director at Huawei and Chairman of the ICT Infrastructure Managing Board, has to argue this way virtually by virtue of his job, he backs up his stance by presenting the top ten industry trends through 2030 at the Global Mobile Broadband Forum (MBBF):
Trend 1
10 Gbit/s for physical-digital integration
In the future, digital communication will expand the exchange of information between people and enable multisensory experiences such as hearing, seeing, touching and smelling. This will require nationwide mobile networks with a data transmission rate of 10 Gbit/s and a latency of one millisecond to transmit information in a more semantically organized way.
Trend 2
One network for 100 billion IoT connections for all scenarios.
By 2030, mobile networks will need to connect up to 100 billion devices. The Internet of Things (IoT), in particular, is forcing network operators to offer different types of connectivity services, differentiated by speed and priority requirements. This means a deterministic experience with lower latency and higher reliability is needed, and a new form of wireless IoT with low power consumption and passive connections must be created.
Trend 3
Collaboration between satellites and stationary networks for 3D coverage.
Collaboration between satellites and fixed networks will fill the gaps in wireless ground coverage and enable three-dimensional airspace coverage, which is needed for communication and control of future drones and aircraft. Mobile networks, with their advanced communications technologies, are playing an increasingly important role in the expansion of satellite communications technologies.
Trend 4
Integrated sensing and communications for true digital twins.
Sensors and communications will be further integrated to enable real-time digital replication of the physical world and facilitate high-level autonomous driving and drone management. Both radio interfaces and network architectures will need to be similarly integrated. Capture resolution technology must advance to the centimeter level through the use of ultra-wideband with Massive MIMO to achieve these functions.
Trend 5
Intelligence in every industry and connection
Wireless networks will be fully integrated with AI technologies to enable fully autonomous Level 5 networks that support automated operations and maintenance and help minimize carbon footprints. Future radios will also be equipped with native intelligence. Intelligent radio algorithms further optimize channel coding and radio resource management.
Trend 6
Green networks with full connectivity and full lifecycle.
As global network traffic increases hundreds of times over the next few years, the demand for solutions that reduce network energy consumption increases just as much. Energy efficiency per bit must also improve at a similar rate. Energy efficiency in particular must be considered in every aspect of network design, including radio interfaces, devices and locations. This is the only way to build these green and sustainable networks throughout their lifecycle.
Trend 7
Flexible full-band below 100 GHz.
By 2030, countries will need an average of 2 GHz of mid-band bandwidth and over 20 GHz of millimeter-wave bandwidth to handle growing data traffic. The industry must facilitate the evolution of sub-100 GHz spectrum to NR (New Radio) and redefine spectrum use through multiband integration and other innovative technologies to achieve a tenfold improvement in spectral efficiency.
Trend 8
Multi-broadband antennas for lower cost per bit
The cost of data transmission per bit could decrease if multi-antenna technologies are used in every frequency band and every scenario. Modular ultra-wideband antennas support flexible combinations of multiple bands. Smart reflective surfaces will apply multi-antenna technologies in more and more scenarios to enable cloud-based deployment.
Trend 9
Security as a cornerstone for a digital future
Intrinsic device security and smart and simplified security at the network level are becoming increasingly important as network security and resilience become more of a global focus. Operators need to offer these types of simplified security services via cloud-network synergies for their industrial customers to drive digital transformation.
Trend 10
Mobile computing networks for device pipe cloud collaboration.
Future mobile networks will support more diverse services, such as the metaverse, industrial field networks and vehicle-to-anything (V2X) communications. This means that data processing must be integrated into mobile networks to provide uninterrupted, high-quality services on demand, as a single service model is not sufficient for building new digital platforms.
Wang rounded out his presentation by reiterating that these ten industry trends are a clear sign that the mobile industry is rapidly moving toward a fully intelligent world. He concluded by promising that Huawei will continue to work with industry partners to define these networks of the future and make the 2030 smart world vision a reality.
To read the full whitepaper, visit Huawei’s page: 10 Trends in the Mobile Industry.





Leave A Comment