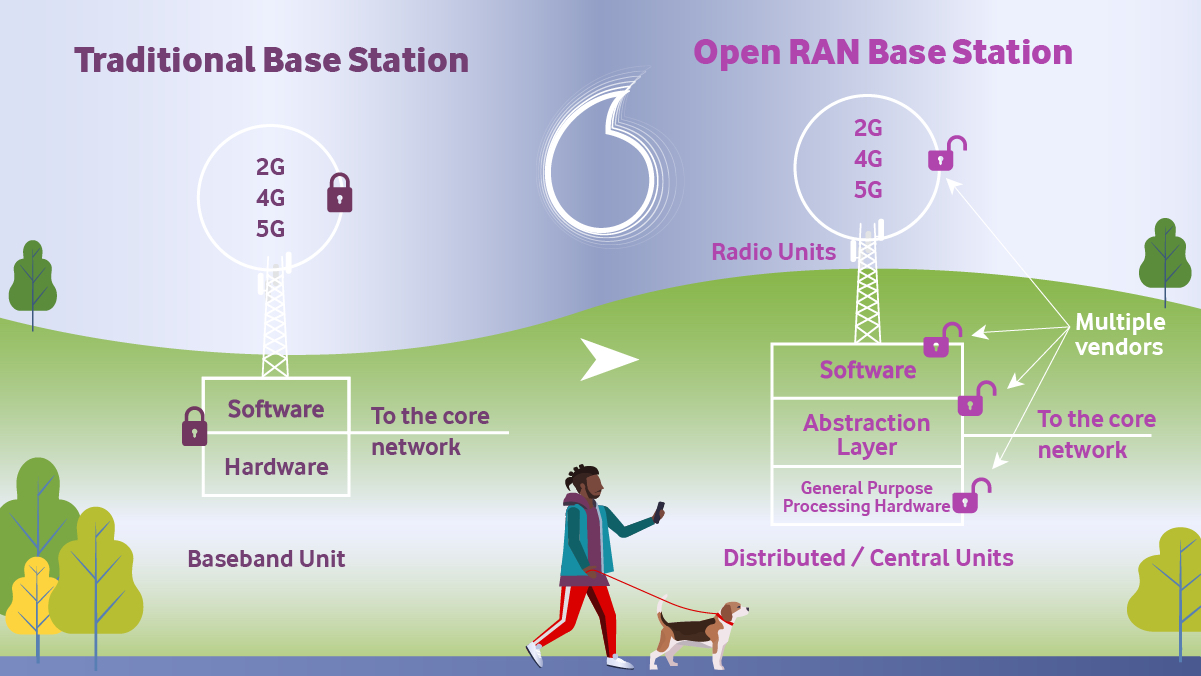
OpenRan (Picture: Vodafone)
Actually, OpenRAN should enable the major mobile operators to supply themselves on the market with interoperable RAN components that come from different manufacturers. But this is obviously not enough for Vodafone. The provider is driving technical development with partners to develop its own OpenRAN modules for its 5G networks.
While Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia enable efficient operation of 5G base stations with specialized chips, the suppliers of OpenRAN components rely almost exclusively on Intel’s x86 platform. The chip technology from the PC and server sector is not adapted to the tasks of a radio network and therefore consumes an unnecessary amount of energy, according to a frequently expressed criticism of the OpenRAN concept.
Vodafone now wants to counter this. In Málaga, Spain, the company opened a research facility for radio technology, in which chip development plays an important role. The team comprises 700 employees, 50 of them in hardware development, 650 work on the appropriate software. The focus partner is Intel, the previous main supplier for Vodafone’s base stations. Even with the x86 standard platform, Intel has a development lead of three years, Vodafone states.
x86, ARM and Risc-V
But other chip developers are also present in the Spanish research institution, half of them from Europe. The mobile provider states that around 20 companies are involved, including Qualcomm, Broadcom, ARM and Lime Microsystems. Santiago Tenorio, director of network architecture at Vodafone, announced that in addition to Intel’s x86 platform, ARM and RISC-V-based chips will also be used in the future.
The facility in Malaga is part of a larger development network in the Vodafone Group. In Newsbury, UK, it operates an “Open RAN Test and Integration Lab”, which opened in April 2021. Here, OpenRAN platforms should be tested and their interoperability validated. Vodafone also wants to offer the services of the testlab to providers and partners, so that the facility becomes part of an evolving OpenRan ecosystem.
“OpenRAN will enable mobile operators to quickly add new digital services and to optimise networks using artificial intelligence (AI). It will bring disruptive innovation back to the network.”
Santiago Tenorio, Director of Network Architecture, Vodafone
In addition, the mobile phone provider had already announced last summer that it would also establish a “skill hub” with 200 employees in Germany. In addition to OpenRAN, the development facilities will also provide solutions in the areas of cybersecurity and mobile private networks (so-called campus networks).
Broad ecosystem for OpenRAN
At the same time as this announcement, Vodafone named a number of partners to help build OpenRAN solutions. These include Dell Technologies, NEC, Samsung, Wind River, Capgemini Engineering and Keysight Technologies.
In the meantime, further partners have been added. Together with Juniper Networks and Parallel Wireless, a multi-vendor RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) was developed that supports OpenRAN interfaces and cloud-native OpenRAN functions. In this way, resource management can be automated and optimized. In addition, the solution offers functions such as multi-tenant access, prioritization for business-critical data traffic and real-time tracking. At the Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona, the solution will be presented as part of Parallel Wireless’ trade fair appearance in Hall 5, Stand 5C61.






Leave A Comment