Ericsson ranked as a leader in 5G technology by Gartner (Source: Ericsson)
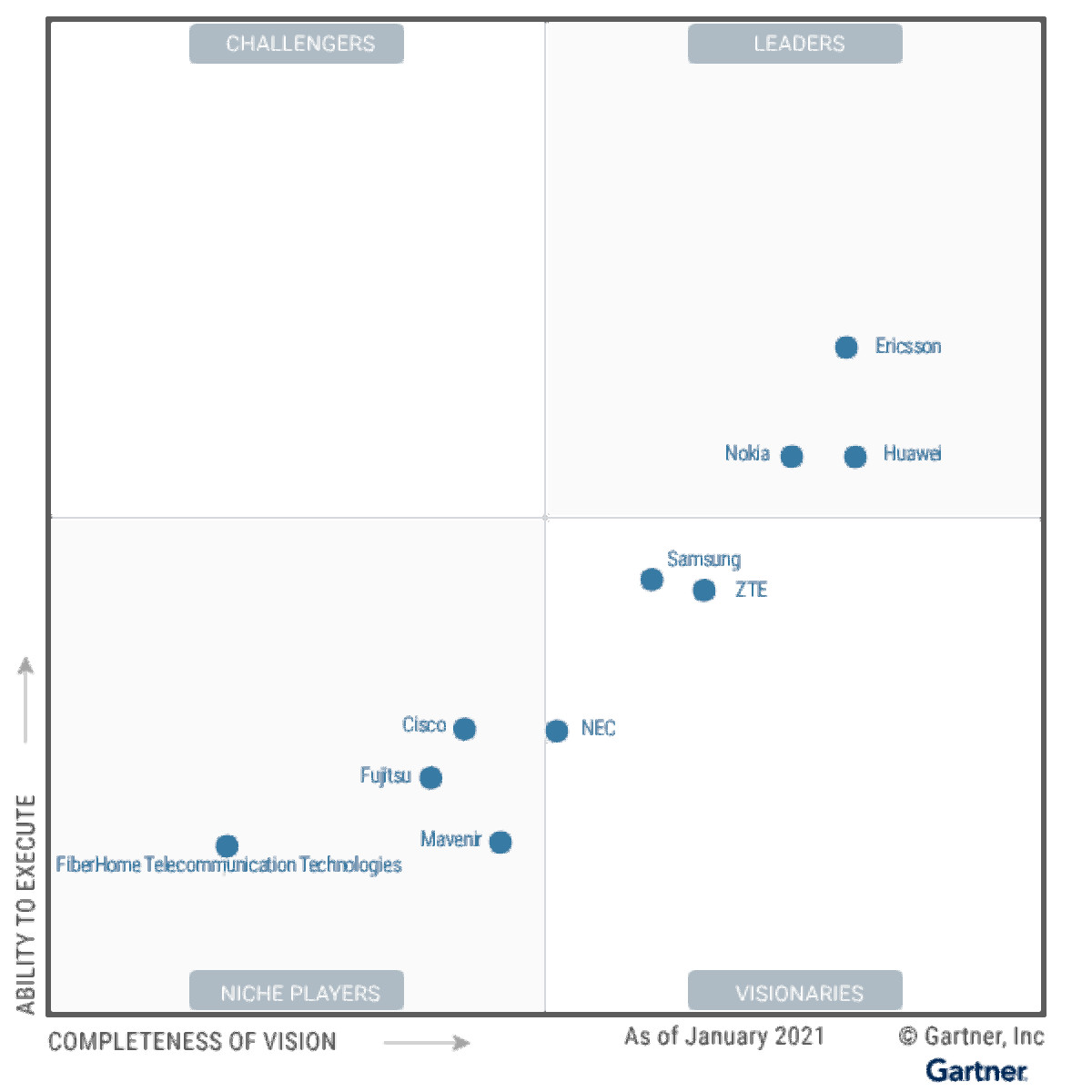
Market researchers at Gartner compared ten providers of 5G network infrastructure. Only three made it into the Leader Quadrant. The classifications of the report are based on an intensive analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the providers.
How do vendors of 5G infrastructure for network providers (communications service providers, CSPs) differ? Who offers the most advanced solutions, how do customers rate the services, and what about the speed of development? Gartner market researchers provide the answers in their latest report, Magic Quadrant for 5G Network Infrastructure for Communications Service Providers.
Clearly defined market definition
Ten suppliers of 5G infrastructure made it into the evaluation:
- Cisco
- Ericsson
- FibreHome Telecommunications Technologies
- Fujitsu
- Huawei
- Mavenir
- NEC
- Nokia
- Samsung
- ZTE
However, the market researchers only included solutions suitable for CSP; solutions for private and local networks, such as campus networks, were not included in this analysis.
Gartner lists RAN equipment, including radio units (RUs) and base band units (BBUs), as well as the core network and evolved packet core (EPC), transport network equipment and network infrastructure services as elements of the infrastructure solutions considered.
Leaders, visionaries and niche players
Ericsson, Huawei and Nokia were the only vendors to have achieved leader status. Samsung, ZTE, and NEC are classified as visionaries, and Cisco, Fujitsu, Mavenir, and FiberHome Telecommunication Technologies are considered niche players, according to Gartner.
The two factors “completeness of vision” and “ability to execute” formed the basis for the classification in the corresponding quadrants. The former was based on more detailed features, such as how they enable IT vendors to be competitive, efficient, and effective, and have a positive impact on revenue, customer retention, and reputation within Gartner’s market vision. The assessment of the ability to execute was based on the size of the portfolio and the services provided by the respective provider.
For example, looking at the Leaders quadrant, Ericsson clearly leads in execution capability, but is narrowly beaten by Huawei, the leader here, in completeness of vision. Nokia is on a par with the Chinese vendor in terms of execution, but falls slightly behind in terms of completeness of vision.
Ericsson in front on execution capability
Gartner credited Ericsson with a leadership role in 5G, in part because of improvements in dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) and uplink booster technology that contributed to its first mover advantage. The market researchers also pointed out that RAN equipment from Ericsson dating back to 2015 can be upgraded to 5G New Radio (NR) via a software update. This, they said, is a clear differentiator that allows customers to deploy 5G networks earlier than competitors.
“From research to rollout, we have invested heavily in 5G to ensure we have the best products, skills and field personnel to meet our customers’ needs. We believe that recognition as a Leader in the Magic Quadrant from Gartner reflects our technology leadership, market competitiveness, determination to innovate and commitment to our customers.”
Fredrik Jejdling, Executive Vice President and Head of Networks, Ericsson
But the report not only mentions tops, but also the downsides in the respective offer. In the case of Ericsson, Gartner lists, among other things, the narrower portfolio of radio units as well as the slower implementation of other features. At the same time, market researchers criticized a lack of flexibility, forcing some CSPs to adapt their roadmaps and deployment priorities to Ericsson’s functional offerings.
The assessment of persecutors Huawei…
Huawei’s continued strong investment in R&D since 2009, as well as its leading contribution to 5G basic patents, is reflected positively in its ranking, as is the great scalability and breadth in its 5G-related portfolio.
On the negative side, the main factor is the ongoing tensions between China and the US. This is weighing on new business, as in some regions the Chinese vendor is completely excluded or there is political controversy over whether Huawei technology should be allowed without restriction. The Gartner experts also warn of possible bottlenecks in the supply of chips due to the U.S. embargo, which could have an impact on the ability to deliver. On the development side, Huawei’s lack of interest in virtualized and Open RAN was noted as a limitation to its overall strategy.
…and Nokia
Nokia, along with Ericsson, is a leader in the signing of trade agreements. With their commitment to virtualized Ran (vRAN), Cloud RAN and Open RAN, the Finns have succeeded in setting themselves off positively from other established suppliers of RAN infrastructure, the market analysts praise. Nokia is also a leader in private LTE and 5G networks.
However, the report also addresses specific weaknesses. For example, there are delays in the further development of the ReefShark chipset. Nokia has meanwhile entered into partnerships with Broadcom, Intel and Marvell to solve this problem. Still, in the case of Nokia solutions, CSPs should keep an eye on chipset development, deployment and product integration, Gartner recommends. The field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) used initially were expensive and delivered lower performance, it said.
The market analysts are also concerned about business trends in developed markets such as China and the U.S. The transition from LTE to 5G has seen the Finns lose market share with some CSPs, which could limit their ability to make product improvements and the business return on early 5G investments.
Detailed statements on opportunities and risks can also be found for other vendors. Free access to the entire report is available via this Ericsson website.








Leave A Comment