With growing concerns about the security of critical infrastructures in mobile communications, the political acceptance of Chinese providers such as Huawei and ZTE is declining. Mobile operators and industrial companies building public and private 5G networks are, therefore, increasingly uncertain about their investment decisions. They are struggling to find similar but safer pastures in Asia to bring their 5G businesses to. The question remains, where to? This company overview lists potential up-and-coming candidates for cross-continent partnerships.
“For the long-term safety of our telecommunications infrastructure, our government has prohibited the inclusion of Huawei and ZTE services”. In May last year, these were some stern words from the Canadian Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry, Francois-Philippe Champagne. Like falling domino stones, the West has already started to join in on this scrutiny of Chinese telecommunication services. Especially, Huawei, the Chinese telecom giant, has been under fire from Western security officials for more than a year over concerns that it poses a cybersecurity threat to Europe and the United States. In the meantime, the company has started to adapt its structures in Central Europe to the declining demand (FUENF-G.de reported, click here to read).
Greener 5G Pastures in South Asia?
Well as of March 2023, Outlook India reported that Indian telecom operators have surpassed the three-year 5G network rollout target given to them within six months. Now, the government is making efforts to enhance the adoption of 5G applications across various industries and key segments.
“It is also about enterprise solutions. A lot of industries can ride on 5G”, VL Kantha Rao, from the Indian Ministry of Communications, told the Press Trust of India. He further elaborated, “we have a set of 100 5G use cases documented and circulated to most of the stakeholders. We have requested ministries and the private sector industry adopt these 5G use cases. That is the next challenge, and we are working very hard on that.”
MWC 2023 recognises India’s mettle
Indian telecommunication companies placed themselves prominently under the limelight at the Mobile World Congress 2023 in Barcelona. Rao proudly expressed, “the very fact that global telecom industry body GSMA has recognised India’s leadership under the current government’s leadership award shows the kind of public-private sector partnership happening in our subcontinent right now”.
The Department of Telecommunications (India) has made one thing clear, GSMA has recognised the way both the Indian government and the industry are working together in developing telecom products in India to supply to the rest of the world. Rao caps off, “the latest example is that the 5G stack is now fully developed in India, ready to be deployed and ready to be exported to any part of the world.”
Bearing this catapulting growth in mind, let’s list the top-tier as well as upcoming Indian telecom companies producing 5G technology, who are ready to form alliances in Europe.
1. Jio Platforms Ltd
Jio Platforms Ltd. is an Indian technology company and a subsidiary of Reliance Industries Limited, headquartered in Mumbai, India. Jio Platforms has an end-to-end 5G solution consisting of 5G Radio, a complete 5G Core Network, AI/ML ATOM platform for 4G/5G, MANO for cloud CNF orchestration, ACI for cloud infrastructure deployment as well as the Cloud-native OSS Platforms.
In addition to these core platforms, Jio Platforms has also created its own cloud-native probing solutions for radio and core networks, simplifying network debugging and not requiring any systems integration with probe providers. To enable a SaaS-based model, JPL has also developed a sophisticated array of BSS solutions.
The entire product line is cloud native and can be deployed either on a public cloud or a private cloud. JIO now has emerged as a market leader in 5G companies in India and abroad.
2. Vodafone Idea
The VI Website for businesses providing integrated IOT solutions and more. (Picture: Vodafone Idea Screenshot)
VI is an Indian phone company that was made when Vodafone India and Idea Cellular joined forces. It is the 10th largest telecom service provider in the world. The company provides pan India Voice and Data services across 2G, 3G, and 4G platforms. The company holds a diverse spectrum portfolio including mid-band 5G spectrum in 17 circles and mmWave 5G spectrum in 16 circles.
VI is developing infrastructure to introduce newer and smarter technologies, making both retail and enterprise customers future ready with innovative offerings, conveniently
accessible through an ecosystem of digital channels as well as an extensive on-ground presence. It has put in place many technologies, such as massive MIMO, DSR, and cloudification of core, that are needed to put 5G services in place. They have tested 5G in two cities with Nokia and Ericsson, their biggest network partners.
3. Bharti Airtel
Airtel 5G test network has come up with a range of diverse use cases across industry verticals. (Picture: Airtel Website Screenshot)
Headquartered in India, Airtel is a global communications solutions provider with over 474 Mn customers in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa. The company ranks amongst the top three mobile operators globally and its networks cover over two billion people. Airtel is India’s largest integrated communications solutions provider and the second-largest mobile operator in Africa. For B2B customers, Airtel offers a gamut of solutions that includes secure connectivity, cloud and data center services, cyber security, IoT, Ad Tech, and cloud-based communication.
Bharti Airtel (“Airtel”), one of India’s premier communications solutions providers, recently rolled out ‘5G for Business’ initiative to demonstrate a wide range of enterprise-grade use cases using high-speed & low latency networks. For this Airtel is joining forces with leading global consulting and technology companies such as Accenture, AWS, CISCO, Ericsson, Google Cloud, Nokia, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) to work with industry-leading brands such as Apollo Hospitals, Flipkart, and several leading manufacturing companies to test 5G based solutions.
These solutions will be deployed on the 5G test spectrum allotted to Airtel and include use cases like Smart Factory, Smart Healthcare, 5G powered Quality inspection, Digital Twin, connected frontline workforce, and AR/VR-based use cases amongst others. Airtel is also spearheading the O-RAN Alliance initiatives in India to build 5G solutions. It has already announced partnerships with Tata Group, Qualcomm, Intel, Mavenir, and Altiostar.
Randeep Singh Sekhon, CTO, of Bharti Airtel says “The 5G ecosystem will open limitless possibilities for enterprises to enhance productivity and serve their customers even better with digitally enabled applications.” Sekhon also shares, “we are delighted to work with our strategic technology partners and some of our enterprise customers to start testing real-life 5G applications of the future. This also offers tremendous learnings across the value chain and lays a solid foundation for future application roadmap.”
4. HFCL
Himachal Futuristic Communications Limited, also known as HFCL, is an Indian telecommunications company founded in 1987. It works with various industries, including telecommunications, security, railways, textiles, and cable fiber.
It is making a line of 5G products, such as 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) and 5G Transport equipment, for both the Indian market and the world market. The 5G RAN portfolio includes Macro Radio units, cell site routers, and aggregation routers. It also wants to take advantage of India’s 1 Billion rupees or c.a. 11 Million Euros (5G) market and export to West Asia, South-East Asia, and Europe.
“We have launched our 5G lab-as-a-service to expedite the process of mandatory testing and certification of new 5G products. Under our in-house R&D, we are designing our own cell site routers, aggregation, and centralized routers, and switches for private and public networks,” said Mahendra Nahata, managing director of HFCL.
5. Sterlite Technologies Ltd
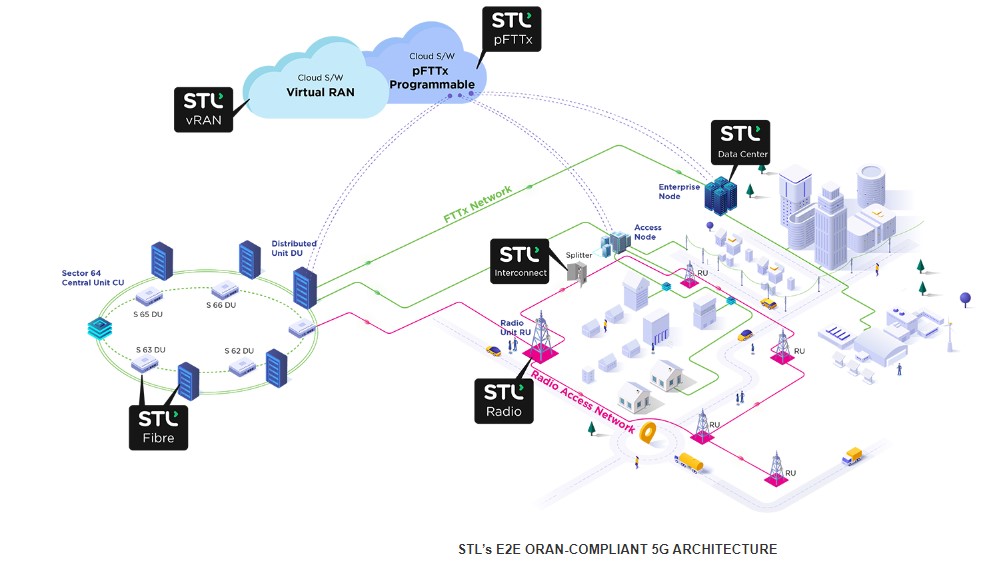
Indian tech company Sterlite Technologies Limited focuses on optical fiber and cables, hyper-scale network design and deployment, and network software. STL has established itself as a global optical and digital solutions company. It provides advanced offerings to build 5G, Rural, FTTx, Enterprise, and Data Centre networks. The company designs and manufactures in four continents, with customers in more than 100 countries.
Telecom operators, cloud companies, citizen networks, and large enterprises recognize and rely on STL for advanced capabilities in Optical Connectivity, Global Services, and Digital and Technology solutions to build ubiquitous and future-ready digital networks. STL’s business goals are driven by customer-centricity, R&D, and sustainability. Championing sustainable manufacturing, the company has committed to achieving Net Zero emissions by 2030.
STL has a strong global presence in India, the Middle East, Italy, the UK, the US, China, and Brazil. The firm intends to construct a 5G network in India and elsewhere by integrating optical and wireless technologies with virtualization and a systematic approach to network deployment.
Why partner with Indian companies?
“There is a unique alignment in the Indian market, where operators and the government are working together,” explained Josh Aroner, Vice President, Global Customer Marketing at Nokia, as to why the Finnish company chose to partner up with Bharti Airtel for 5G deployment. He also noted that the Indian market is also familiar with the variety of B2B use cases of 5G and added that once 5G for enterprises is made available the deployment of enterprise applications will occur very quickly.
As the capital expenditure for 5G commences, India is emerging to be the second-largest market for telecom in the world. Aroner noted that the Indian industry is also uniquely suited for enterprise applications since it is younger than the western markets. “Indian industry has already accepted digitisation which could facilitate enterprise applications of 5G in the future,” Aroner concluded. Just like Nokia, multiple inter-continental partnerships have already blossomed and many more await. For European companies to pan away from the overbearing influence of China and concentrate more on emerging powers like India, could be a strategically sound move.
Given India’s political distance from China, Europe’s cybersecurity concerns can be addressed, by shifting their businesses to a country with similar resources but safer methods. It remains to be seen, which fruitful collaborations come up in the future and whether the World feels confident enough to test the mettle of Indian telecommunications.
To read more about the Huawei scandal, read Huawei: Retreat in stages?
Read more about why India’s 5G market is particularly lucrative for telecom companies.







Leave A Comment